Education
Translation 101: Your Guide to Becoming a Successful Translator

Are you fascinated by languages, cultures, and the art of communication? Do you find yourself drawn to the idea of bridging the gap between people who speak different languages? If so, you might have what it takes to become a successful translator. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the fundamentals of translation, the skills you need, and the steps to kickstart your career. Whether you’re an aspiring translator or looking to enhance your existing skills, this article will provide valuable insights and guidance.
Understanding the World of Translation
What is Translation?
The first step to learning how to become a translator is learning what translation is. Translation is the process of converting written or spoken content from one language to another while maintaining its original meaning, tone, and context. Translators play a crucial role in facilitating global communication, making information accessible to a wider audience, and promoting cross-cultural understanding.
The Importance of Translation
Translation is essential in various industries, such as business, medicine, law, literature, and diplomacy. It helps people overcome language barriers and facilitates international trade, diplomacy, and cultural exchange. Accurate translation can also be a matter of life and death in the medical field or a deal-breaker in business negotiations.
Skills Required for Translation
Proficiency in Source and Target Languages
To become a successful translator, you must be highly proficient in both your source (the language you’re translating from) and your target (the language you’re translating into) languages. A deep understanding of grammar, vocabulary, idiomatic expressions, and cultural nuances is crucial.
Attention to Detail
The devil is in the details. Translators must pay close attention to every word, phrase, and sentence to ensure accuracy and consistency in their work. A small mistake can change the entire meaning of a text.
Cultural Sensitivity
Language is deeply intertwined with culture. Translators need to be culturally sensitive to ensure that the translation reflects the cultural context of the source language. This includes understanding customs, idioms, and the broader cultural implications of language choices.
Research Skills
Translators often encounter unfamiliar terms, concepts, or technical jargon. Strong research skills are essential for finding accurate and contextually appropriate translations. Reliable resources like dictionaries, glossaries, and subject matter experts can be invaluable.
Time Management
Deadlines are a constant in the world of translation. Effective time management skills are crucial to meet client expectations and maintain a steady workflow.
Writing and Editing Skills
Translators are not just converters of text; they are also writers. A successful translator should be able to write in a clear and engaging manner, and they must possess strong editing skills to polish their translations.
Getting Started as a Translator
Education and Training
While a formal education in translation or a related field can be helpful, it’s not always necessary. Many successful translators are self-taught. If you decide to pursue formal education, look for programs that offer coursework in your specific language pair.
Build Your Language Skills
If you’re not already proficient in both your source and target languages, invest time in honing your language skills. Take language courses, immerse yourself in the culture, and practice speaking, reading, and writing regularly.
Choose Your Specialization
Translation is a broad field, and many translators choose to specialize in a particular area. Some common specializations include legal, medical, technical, literary, and business translation. Choose a specialization that aligns with your interests and expertise.
Gain Experience
To build your reputation as a translator, you need practical experience. Consider offering your services pro bono to build your portfolio or work as an intern. You can also take on small freelance projects to gain experience and testimonials.
Build a Portfolio
A strong portfolio showcases your translation skills and demonstrates your expertise to potential clients. Include a variety of translation samples that highlight your proficiency and specialization. Your portfolio will be a key marketing tool.
Tools of the Trade
Translation Software
Translation software, such as CAT (Computer-Aided Translation) tools, can significantly enhance your efficiency and accuracy. Popular options include SDL Trados, memoQ, and OmegaT. These tools help you manage terminology, maintain consistency, and speed up your workflow.
Dictionaries and Glossaries
Online and offline dictionaries, glossaries, and specialized terminology resources are invaluable for research and reference during translation. Invest in high-quality language resources that are specific to your specialization.
Style Guides
Different clients and industries may have their own preferred style guides. Familiarize yourself with commonly used guides like The Chicago Manual of Style, APA, or industry-specific style guides to ensure your translations meet their requirements.
Time Management Tools
Effective time management is essential for meeting deadlines. Tools like task management apps and time tracking software can help you stay organized and on schedule.
The Translation Process
Pre-Translation Preparation
Before diving into the translation itself, take time to understand the context, purpose, and audience of the content. Familiarize yourself with any relevant industry or subject matter, and make a plan for handling potential challenges.
Translation
During the translation process, focus on conveying the original message accurately while adapting it to the target language and culture. Pay attention to grammar, syntax, vocabulary, and cultural nuances.
Editing and Proofreading
After the initial translation is complete, it’s essential to review and edit your work for clarity, accuracy, and style. Proofreading helps eliminate any errors or inconsistencies.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a critical step. Ensure that the translation reads naturally, is culturally appropriate, and conveys the intended message. It’s also important to check for any formatting or layout issues that may arise during the translation process.
Client Communication
Maintaining clear and open communication with your client is crucial. Seek feedback and clarification when needed, and keep the client informed about your progress and any potential issues.
Marketing Your Translation Services
Create a Professional Online Presence
Build a professional website or create profiles on freelance platforms and translation directories. These online platforms will serve as your digital business card and portfolio.
Networking
Connect with fellow translators, attend industry conferences, and engage with potential clients through social media and networking events. Building a strong professional network can lead to new opportunities.
Cold Pitching
Don’t wait for clients to come to you. Reach out to potential clients and agencies with a well-crafted pitch that showcases your skills and expertise. Be persistent and follow up when necessary.
Pricing Your Services
Determine your pricing structure based on factors like your specialization, experience, and the complexity of the project. Be transparent with your pricing and billing practices.
Handling Challenges
Dealing with Ambiguity
Languages are not always clear-cut, and translations may encounter ambiguous or complex passages. In such cases, consult with subject matter experts or seek additional context from the client.
Staying Current
Languages and industries evolve. Stay up to date with language trends, cultural changes, and industry developments to ensure your translations remain accurate and relevant.
Burnout Prevention
The demands of translation work can be intense. Set realistic boundaries, take breaks, and manage your workload to prevent burnout. Prioritize self-care to maintain your well-being.
Certification and Accreditation
Consider Certification
Some clients and agencies may require or prefer translators with professional certifications. Organizations like the American Translators Association (ATA) offer certification exams that can enhance your credibility.
Continuing Education
Translation is a lifelong learning process. Invest in ongoing education and professional development to stay at the top of your game.
Conclusion
Becoming a successful translator is a journey that requires dedication, continuous learning, and a passion for languages and cultures. Armed with the right skills, tools, and strategies, you can carve out a rewarding career in this dynamic field. Remember that the world of translation is ever-evolving, so stay adaptable, open to new challenges, and committed to delivering the best possible translations for your clients. With persistence and dedication, you can turn your love for languages into a successful and fulfilling profession as a translator. Good luck on your translation journey!
Education
ABCDX Segmentation: Boost Customer Interaction and Sales

Introduction
In today’s competitive market, understanding and optimizing customer relationships is crucial for business success. One powerful tool for achieving this is ABCDX segmentation. This approach helps businesses categorize their customers into distinct groups based on their payment behavior and interaction with support. By effectively utilizing ABCDX segmentation, companies can enhance customer satisfaction, streamline support efforts, and ultimately boost sales.
Understanding ABCDX Segmentation
Definition and Origin
ABCDX segmentation is a method used to classify customers into five distinct segments: A, B, C, D, and X. Each segment represents a different level of engagement and value to the business. This segmentation approach allows companies to tailor their marketing and support strategies to meet the specific needs of each group.
The Five Segments: A, B, C, D, X
- Segment A: Ideal clients who are highly engaged and satisfied.
- Segment B: Regular users with some objections or comments.
- Segment C: Clients with low engagement and small transaction volumes.
- Segment D: Low-interest clients who use up valuable resources.
- Segment X: Potential Segment A clients who need product modifications.
Segment A: Ideal Clients
Characteristics of Segment A
Segment A clients are the cream of the crop. They are highly interested in the product, make frequent purchases, and have a short transaction cycle. They are also low maintenance when it comes to support, as they are generally satisfied with the product.
Benefits of Targeting Segment A
Focusing on Segment A clients can lead to increased sales and customer loyalty. These clients are likely to provide positive word-of-mouth referrals and contribute to a stable revenue stream.
Strategies for Engaging Segment A
To maintain and grow your relationship with Segment A clients, consider implementing loyalty programs, personalized marketing efforts, and exclusive offers. Ensuring their continued satisfaction can lead to long-term success.
Segment B: Engaged but Critical Clients
Characteristics of Segment B
Segment B clients are engaged with the product but have specific objections or feedback. They make regular purchases and have a short transaction cycle but expect improvements or adjustments.
How to Address Objections and Comments
Actively listen to Segment B clients’ feedback and address their concerns promptly. Implementing changes based on their input can enhance their satisfaction and foster loyalty.
Enhancing Relationships with Segment B
Engage Segment B clients with personalized communication and tailored solutions. Offering exceptional customer service can turn their critical feedback into opportunities for growth.
Segment C: Low-Engagement Clients
Characteristics of Segment C
Segment C clients have a long transaction cycle and make small purchases. They may not be fully satisfied with the product or its fit for their needs, leading to lower engagement levels.
Challenges with Segment C
Managing Segment C clients can be challenging due to their low engagement and high likelihood of attrition. They may also require more resources for support and sales efforts.
Strategies for Improving Engagement
To increase engagement with Segment C clients, consider offering targeted promotions, improving product features, and enhancing customer support. Understanding their needs and addressing them effectively can lead to better results.
Segment D: Low-Interest Clients
Characteristics of Segment D
Segment D clients are minimally interested in the product and require significant time and resources for support. They rarely make purchases and may be a drain on sales and support teams.
Impact on Sales and Support
Segment D clients can affect overall business performance by consuming resources without contributing significantly to revenue. It’s important to manage these clients efficiently to minimize their impact.
Strategies for Managing Segment D
Consider strategies such as reducing support efforts for Segment D clients, focusing on other segments, or even reevaluating their fit for the product. Streamlining processes can help mitigate their impact.
Segment X: Potential Ideal Clients
Characteristics of Segment X
Segment X clients show potential to become Segment A but currently find the product unsuitable. They often request modifications or improvements, indicating a need for product adjustments.
Identifying Opportunities for Improvement
Analyze feedback from Segment X clients to identify common themes and areas for improvement. Tailoring your product to meet their needs can convert them into high-value clients.
Developing Strategies to Convert Segment X
Engage Segment X clients through targeted trials, personalized offers, and product enhancements. Demonstrating a commitment to meeting their needs can encourage their transition to Segment A.
Implementation of ABCDX Segmentation
Steps for Segmenting Your Audience
- Collect and analyze customer data.
- Define criteria for each segment based on payment behavior and support interaction.
- Categorize customers into the appropriate segments.
- Develop targeted strategies for each segment.
Tools and Technologies for ABCDX Segmentation
Utilize CRM systems, analytics platforms, and marketing automation tools to effectively manage and analyze your customer segments. These technologies can streamline segmentation and enhance targeting efforts.
Case Studies and Examples
Explore case studies of companies that have successfully implemented ABCDX segmentation. Analyze their strategies and outcomes to gain insights and apply similar approaches to your business.
Benefits of ABCDX Segmentation
Improved Customer Satisfaction
By addressing the specific needs of each segment, businesses can enhance overall customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Enhanced Sales Performance
Targeting the right segments with tailored strategies can lead to increased sales and revenue.
Efficient Resource Allocation
Segmentation helps businesses allocate resources more effectively, focusing efforts where they will have the greatest impact.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges in ABCDX Segmentation
- Difficulty in accurately categorizing customers.
- Managing diverse needs across multiple segments.
- Ensuring consistent and effective communication.
Solutions and Best Practices
- Use advanced analytics to improve segmentation accuracy.
- Develop clear strategies for each segment.
- Regularly review and adjust segmentation criteria based on performance.
Future Trends in Customer Segmentation
Emerging Trends in Segmentation
Stay ahead of trends such as hyper-personalization, predictive analytics, and AI-driven insights. These advancements can enhance your segmentation efforts and drive better results.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies are transforming customer segmentation by providing deeper insights and automating processes. Leveraging these technologies can improve accuracy and efficiency.
Conclusion
ABCDX segmentation offers a powerful approach to understanding and optimizing customer relationships. By effectively categorizing customers and tailoring strategies to each segment, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction, boost sales, and allocate resources more efficiently. Embrace the ABCDX model to unlock the full potential of your customer interactions and drive business success.
FAQs
What is the main goal of ABCDX Segmentation?
The goal is to categorize customers into distinct segments to tailor marketing and support strategies, improving satisfaction and driving sales.
How can I implement ABCDX Segmentation in my business?
Collect customer data, define criteria for each segment, categorize customers, and develop targeted strategies for each group.
What are the benefits of focusing on Segment A?
Segment A clients are highly engaged and satisfied, leading to increased sales, customer loyalty, and positive referrals.
How do I convert Segment X into Segment A?
Analyze feedback from Segment X, identify opportunities for product improvements, and engage them with tailored solutions and trials.
What tools are best for managing ABCDX Segmentation?
CRM systems, analytics platforms, and marketing automation tools are essential for managing and analyzing customer segments effectively.
Education
Why Think-Feel-Do Is Key in Strategic Marketing Communication

Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of marketing, understanding how to effectively communicate with your audience is crucial. The Think-Feel-Do framework stands out as a proven model for strategic marketing communication. This approach helps marketers craft messages that resonate on multiple levels, ensuring they not only capture attention but also drive meaningful action. In this article, we will explore why the Think-Feel-Do framework is indispensable for modern marketing strategies.
Understanding the Think-Feel-Do Framework
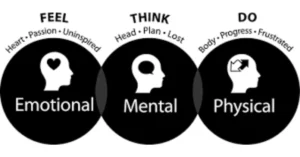
Think: Cognitive Engagement
The “Think” phase involves engaging your audience’s cognitive processes. It’s about what your audience is thinking when they encounter your marketing message. This phase focuses on delivering clear, compelling information that educates and informs.
- What does “Think” involve?
- This step requires understanding your audience’s needs and delivering relevant, valuable content.
- Importance of targeting thoughts
- Engaging the mind is crucial for making an initial impact and positioning your brand as a valuable resource.
Feel: Emotional Connection
Emotions play a pivotal role in decision-making. The “Feel” phase is about connecting with your audience on an emotional level.
- The role of emotions in marketing
- Emotional responses can significantly influence purchasing decisions, making it essential to tap into your audience’s feelings.
- Building emotional resonance
- Crafting messages that evoke feelings of trust, excitement, or empathy can enhance brand loyalty and customer engagement.
Do: Actionable Outcomes
The final phase, “Do,” focuses on driving action. This involves encouraging your audience to take specific steps, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter.
- Driving consumer actions
- Effective marketing strategies must include clear calls to action that guide the audience toward the desired behavior.
- Measuring effectiveness
- Assessing the success of your strategies involves tracking key metrics to see how well you’re converting engagement into actions.
The History and Evolution of Think-Feel-Do
The Think-Feel-Do framework has been a staple in marketing communication for decades. Its origins can be traced back to early psychological studies on consumer behavior and decision-making processes. Over time, the framework has evolved to accommodate changes in technology and media, adapting to digital and social media landscapes.
Implementing Think-Feel-Do in Modern Marketing
Adapting the Think-Feel-Do framework to modern digital channels involves leveraging new tools and platforms.
- Adapting to digital channels
- Digital marketing offers new opportunities for engagement, from social media to email campaigns. Tailoring the Think-Feel-Do approach to these channels can enhance its effectiveness.
- Case studies of successful implementation
- Brands like Nike and Apple have effectively used this framework to drive their marketing strategies, demonstrating its versatility and impact.
Benefits of Using the Think-Feel-Do Framework

Utilizing the Think-Feel-Do framework offers several advantages:
- Enhanced customer understanding
- By focusing on what customers think, feel, and do, marketers can gain a deeper understanding of their audience’s motivations.
- Improved communication strategies
- Tailoring messages to address all three phases ensures a comprehensive approach to customer engagement.
- Increased ROI
- Effective implementation can lead to higher conversion rates and better returns on marketing investments.
Challenges and Solutions
While the Think-Feel-Do framework is powerful, it comes with its own set of challenges.
- Common pitfalls
- Overlooking one of the phases or failing to adapt to audience changes can hinder effectiveness.
- Strategies to overcome challenges
- Regularly reviewing and adjusting your approach based on feedback and performance metrics can help mitigate these issues.
Think-Feel-Do in Different Sectors
The Think-Feel-Do framework is versatile and can be applied across various sectors.
- Retail
- In retail, the framework can help drive purchases by addressing customer needs and emotions at different stages of the buying process.
- Services
- For service-based industries, focusing on the emotional connection and actionable outcomes can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- B2B
- In B2B marketing, understanding the decision-making process and crafting targeted messages can lead to more successful business relationships.
Tools and Techniques for Think-Feel-Do Implementation
Several tools and techniques can aid in the implementation of the Think-Feel-Do framework.
- Analytics and tracking tools
- Tools like Google Analytics and CRM systems can help track engagement and conversion metrics, providing insights for optimization.
- Creative techniques for engagement
- Innovative content formats, such as interactive videos or personalized emails, can enhance emotional and cognitive engagement.
Future Trends in Think-Feel-Do Marketing
The future of marketing will likely see continued evolution in how the Think-Feel-Do framework is applied.
- Emerging technologies
- Advancements in AI, machine learning, and data analytics will provide new opportunities for refining and personalizing marketing strategies.
- Predictions for the future
- As consumer behavior evolves, the Think-Feel-Do framework will need to adapt, incorporating new insights and technologies to remain effective.
Conclusion
The Think-Feel-Do framework remains a cornerstone of strategic marketing communication due to its comprehensive approach to engaging audiences. By addressing cognitive, emotional, and actionable aspects of customer interactions, marketers can craft more effective and impactful campaigns. As the marketing landscape continues to evolve, revisiting and refining this framework will be essential for staying ahead.
FAQs
What is the Think-Feel-Do framework?
The Think-Feel-Do framework is a model used in marketing communication that focuses on engaging customers’ thoughts, emotions, and actions to drive effective outcomes.
How can I implement Think-Feel-Do in my marketing strategy?
Implement the framework by tailoring your content to address what your audience thinks, feels, and does, using data and insights to guide your approach.
What are the benefits of using Think-Feel-Do?
Benefits include a deeper understanding of customer behavior, improved communication strategies, and increased return on investment.
What are some examples of Think-Feel-Do in action?
Examples include successful campaigns by brands like Nike and Apple, which effectively engage customers through thoughtful, emotional, and actionable messaging.
How does Think-Feel-Do compare to other marketing frameworks?
Unlike some frameworks that focus on only one aspect of engagement, Think-Fe’el-Do provides a holistic approach by addressing cognitive, emotional, and behavioral components.
Education
The Psychology Behind Testimonials in Propaganda

Introduction
In the realm of communication and persuasion, propaganda often employs a variety of techniques to influence public opinion. Among these techniques, testimonials play a crucial role. By understanding the psychology behind testimonials in propaganda, we can better grasp how these endorsements shape our perceptions and beliefs.
Understanding Testimonials
What is a Testimonial?
A testimonial is a statement or endorsement given by an individual or group that supports a product, idea, or cause. In propaganda, testimonials are used to lend credibility and emotional weight to a message. These endorsements can come from various sources, including satisfied customers, celebrities, or experts.
Types of Testimonials
- Personal Endorsements: These are testimonials from ordinary individuals who share their personal experiences. Their authenticity often resonates with the audience, making the message more relatable.
- Celebrity Endorsements: When a well-known figure supports a cause or product, it can leverage their fame and influence to persuade others. Celebrity testimonials can significantly boost the perceived value and trustworthiness of the message.
- Expert Opinions: Testimonials from experts in a field can provide authoritative backing to a message. Their knowledge and credentials add a layer of credibility that can be highly persuasive.
The Role of Testimonials in Propaganda
Building Credibility
Testimonials help build credibility by providing evidence that others have had positive experiences. In propaganda, this can translate to increased trust in the message being promoted. When people see that others, especially those they respect or relate to, endorse a cause, they are more likely to believe in it.
Emotional Appeal
Testimonials often evoke emotions, whether through personal stories or enthusiastic endorsements. This emotional connection can make the propaganda more compelling and memorable, as emotions often drive decision-making more than rational arguments alone.
Influencing Perceptions
By showcasing favorable testimonials, propaganda can shape public perceptions of a product, idea, or political stance. This influence can steer public opinion in a desired direction, reinforcing the desired narrative.
Psychological Mechanisms Behind Testimonials
Trust and Authority
People tend to trust individuals who seem authoritative or knowledgeable. Testimonials from experts or celebrities often play on this psychological bias, leveraging their perceived authority to lend weight to the message.
Social Proof
The concept of social proof suggests that individuals are influenced by the behaviors and endorsements of others. When a testimonial reflects a broad consensus or popular opinion, it can reinforce the idea that the message is widely accepted and correct.
Cognitive Dissonance
Testimonials can also address cognitive dissonance, a psychological state where holding conflicting beliefs creates discomfort. By providing reassuring testimonials, propaganda can help resolve this discomfort and align public opinion with the promoted message.
Testimonials and Persuasion
The Persuasive Power of Testimonials
Testimonials are a powerful tool in persuasion because they offer a form of validation. When people hear positive feedback from others, it reduces skepticism and increases the likelihood of acceptance. This technique is frequently used in marketing, politics, and social campaigns to sway opinions and behaviors.
Case Studies and Examples
- Historical Examples: During World War II, propaganda often used testimonials from soldiers and veterans to promote enlistment and boost morale. These personal stories added authenticity and emotional weight to the messages.
- Modern Examples: In contemporary marketing, brands frequently use customer testimonials to highlight the benefits of their products. Positive reviews and endorsements can significantly impact consumer purchasing decisions.
Ethical Considerations
Manipulation vs. Genuine Endorsement
One of the major ethical concerns with testimonials in propaganda is the line between genuine endorsement and manipulation. While testimonials can offer authentic praise, they can also be used to deceive or manipulate the public by presenting biased or misleading information.
The Impact on Public Opinion
The ethical use of testimonials can influence public opinion positively, fostering trust and informed decision-making. Conversely, deceptive or manipulative testimonials can lead to misinformation and skewed perceptions, impacting public trust and societal outcomes.
Analyzing the Effectiveness of Testimonials in Propaganda
Measuring Impact
To assess the effectiveness of testimonials in propaganda, it’s essential to measure their impact on public opinion and behavior. This can involve analyzing changes in attitudes, behaviors, and overall engagement with the message.
Success Stories and Failures
Successful testimonials often lead to increased credibility and support for the message. However, failures can occur if the testimonials are perceived as insincere or if they don’t resonate with the target audience. Understanding these outcomes can provide valuable insights into how to use testimonials effectively.
Strategies for Creating Effective Testimonials
Crafting Authentic Testimonials
To maximize the impact of testimonials, they should be authentic and relatable. Genuine endorsements that reflect real experiences are more likely to build trust and persuade the audience.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Common pitfalls in creating testimonials include using overly promotional language, presenting testimonials that lack credibility, or failing to address potential counterarguments. Avoiding these issues can enhance the effectiveness of testimonials in propaganda.
Future Trends in Testimonial Usage in Propaganda
Digital and Social Media Influence
With the rise of digital and social media, testimonials are increasingly shared and amplified online. This trend can enhance the reach and impact of testimonials but also raises concerns about authenticity and the potential for viral misinformation.
Emerging Technologies
Advancements in technology, such as deepfakes and synthetic media, may influence the future of testimonials in propaganda. These technologies can create realistic but fabricated endorsements, posing new challenges for authenticity and trust.
Conclusion
Testimonials play a significant role in propaganda by leveraging credibility, emotional appeal, and psychological mechanisms to influence public opinion. While they can be a powerful tool for persuasion, their ethical use is crucial in ensuring that they contribute positively to public discourse. Understanding the psychology behind testimonials can help us navigate and critically assess the messages we encounter.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of testimonials in propaganda?
The main purpose of testimonials in propaganda is to lend credibility and emotional weight to a message, making it more persuasive and influential.
How do testimonials influence people’s decisions?
Testimonials influence decisions by providing validation through others’ experiences, creating trust, and appealing to emotions and social proof.
Can testimonials be misleading?
Yes, testimonials can be misleading if they are manipulated or presented without full context, leading to biased or false impressions.
What are some famous examples of testimonials in propaganda?
Historical examples include war-time enlistment campaigns with soldier testimonials, and modern examples include customer reviews and endorsements in advertising.
How can one create an effective testimonial?
To create an effective testimonial, ensure it is authentic, relatable, and reflects genuine experiences while avoiding overly promotional language.
-

 Fashion2 years ago
Fashion2 years agoExploring Purenudism: Embracing Body Positivity and Freedom
-

 Shops1 year ago
Shops1 year agoWalgreen Pharmacy Hours: What Time Does It Open & Close?
-

 Shops2 years ago
Shops2 years agoWalmart Vision Center Hours
-

 Shops1 year ago
Shops1 year agoStaples Store Hours: What Time Does Staples Open And Close?
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoThothub.lol: The Digital Realm of Entertainment
-

 Shops1 year ago
Shops1 year agoPublix Pharmacy Hours and Locations
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoDesigner Clothing: Making a Statement
-

 Shops1 year ago
Shops1 year agoWalmart Deli Open & Close Hours
